📌
What is a Computer Network?

🧠
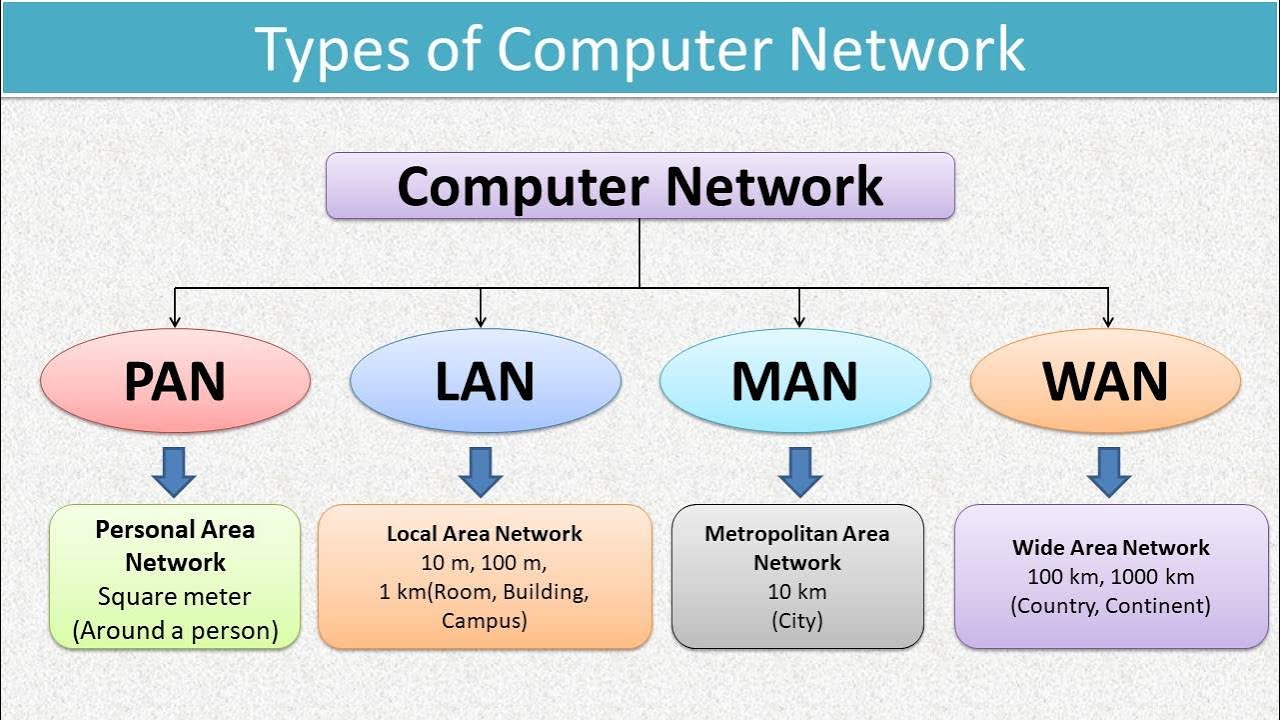
Types of Networks
| Type | Full Form | Range | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
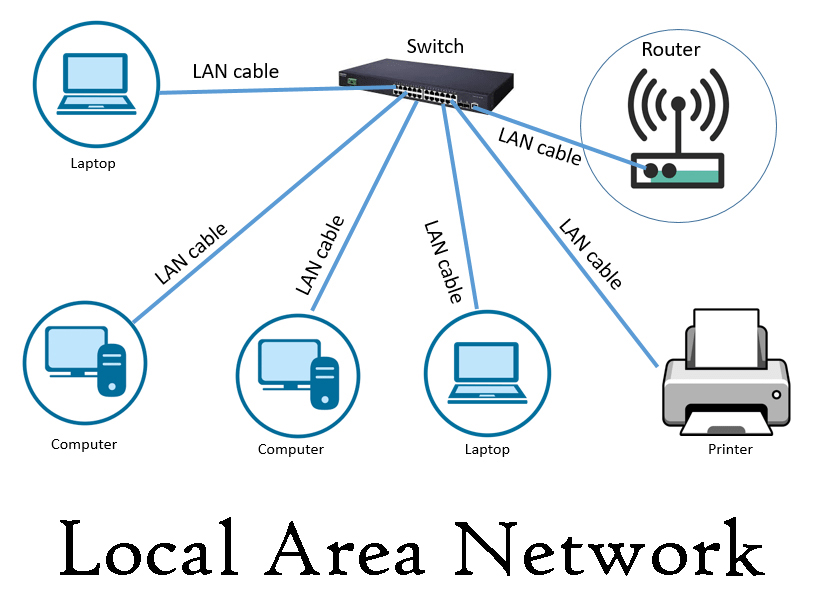
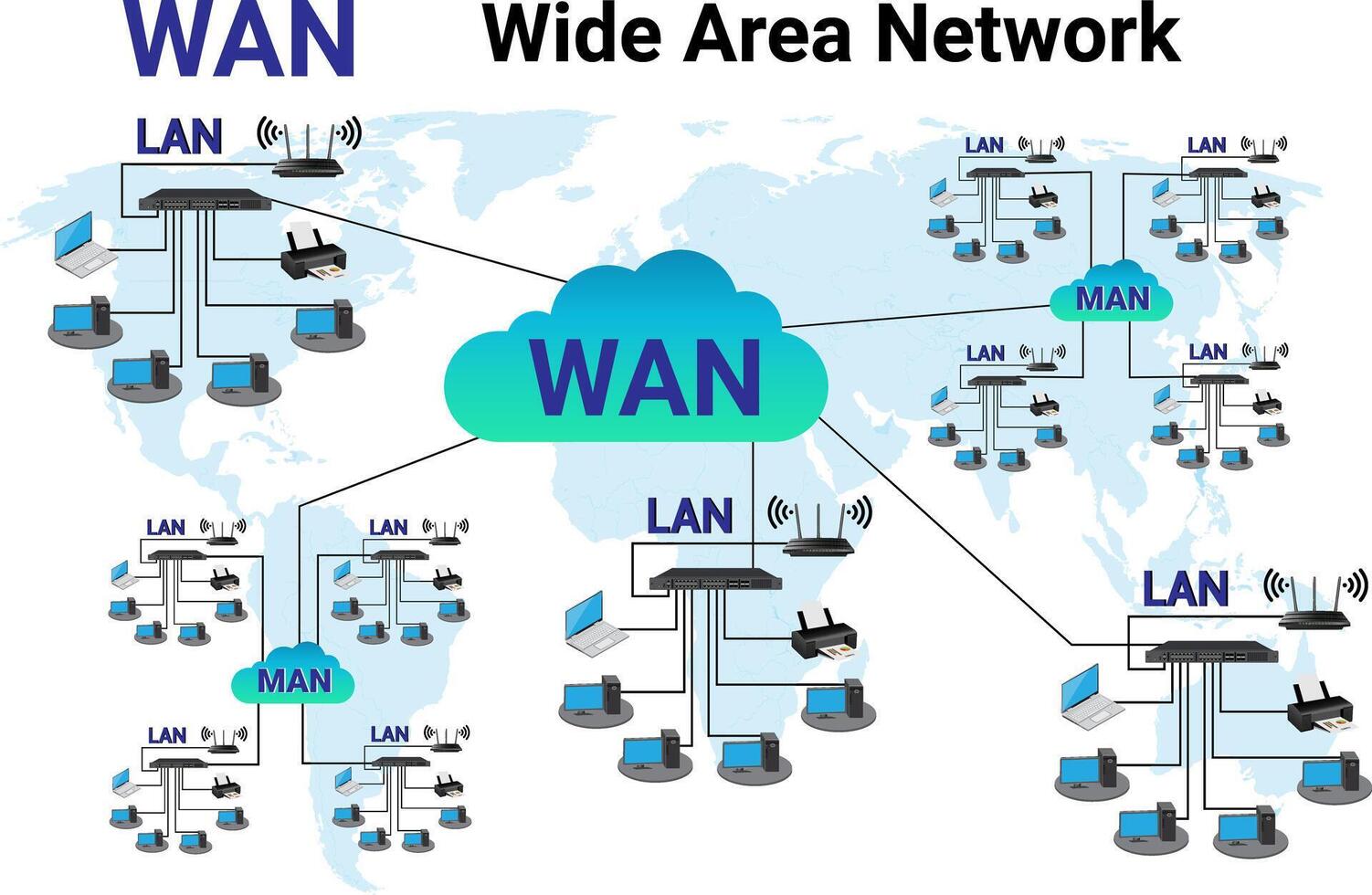
| LAN | Local Area Network | Up to a few kilometers | Offices, Schools |
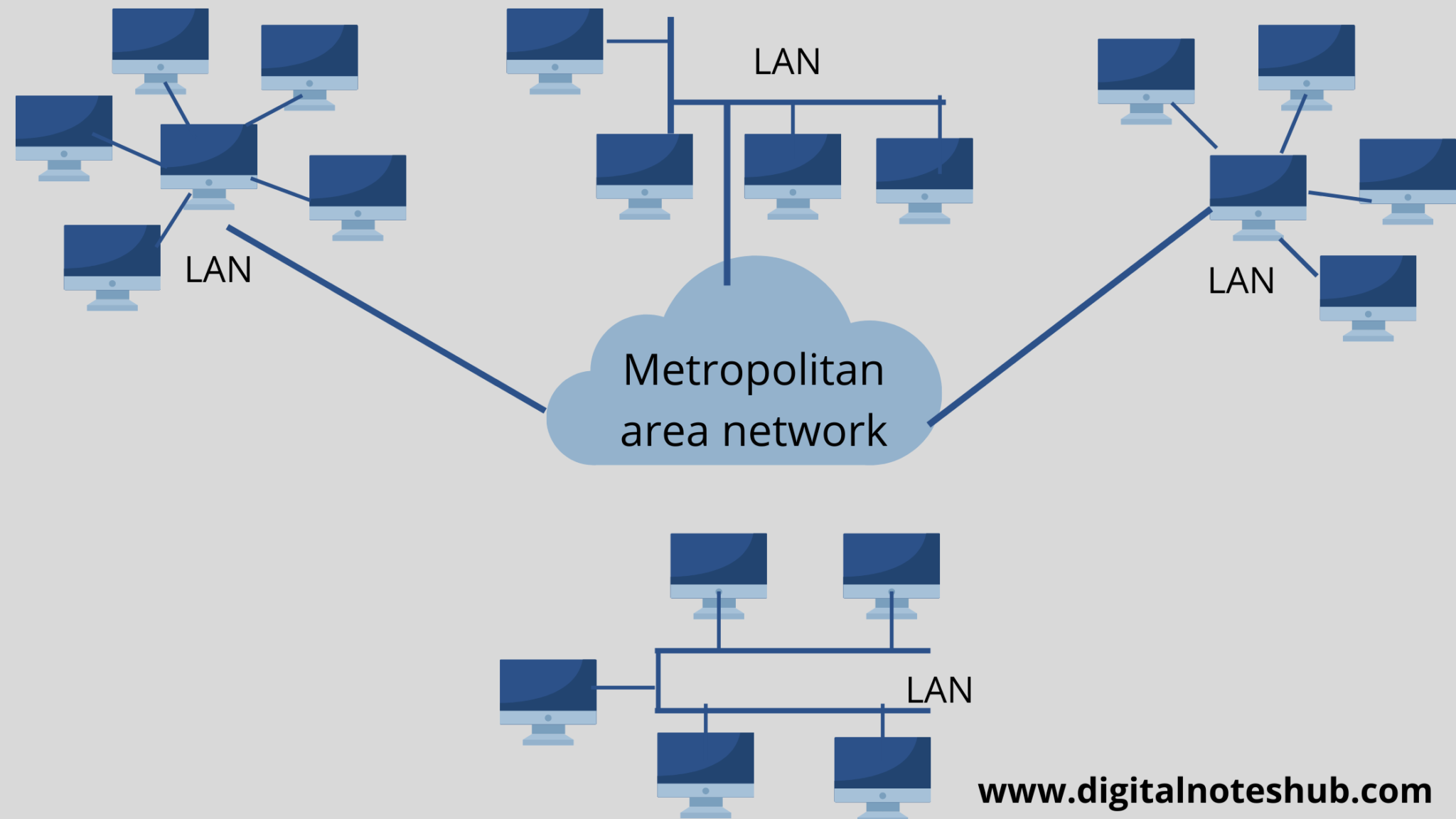
| MAN | Metropolitan Area Network | Covers a city | Cable TV network in a city |
| WAN | Wide Area Network | Covers countries | Internet |
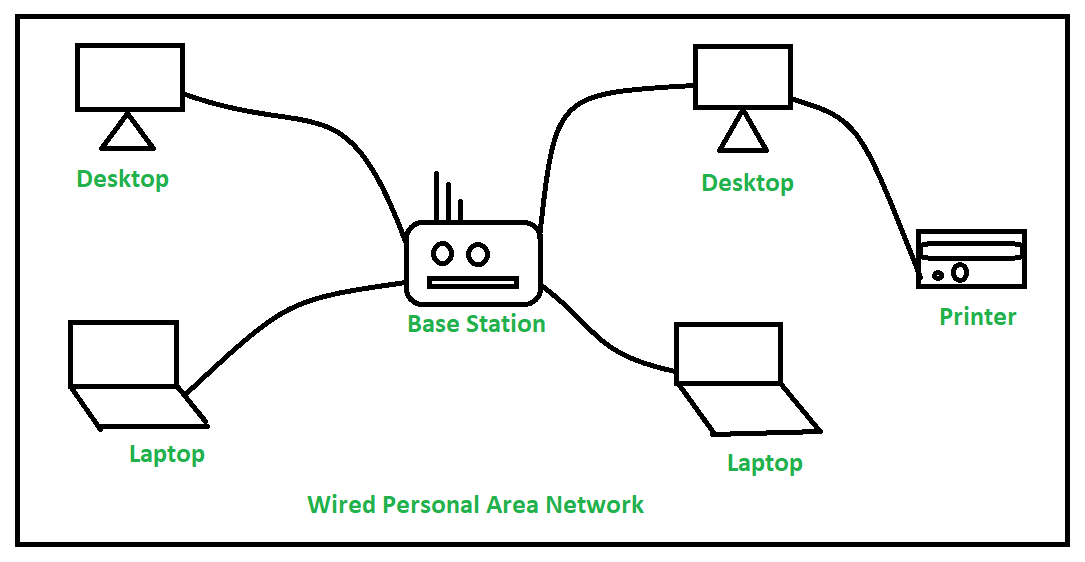
| PAN | Personal Area Network | Few meters | Bluetooth, USB cable |
🌐
Network Topologies
What is Topology?
Topology = Arrangement of different elements (devices, nodes) in a network.
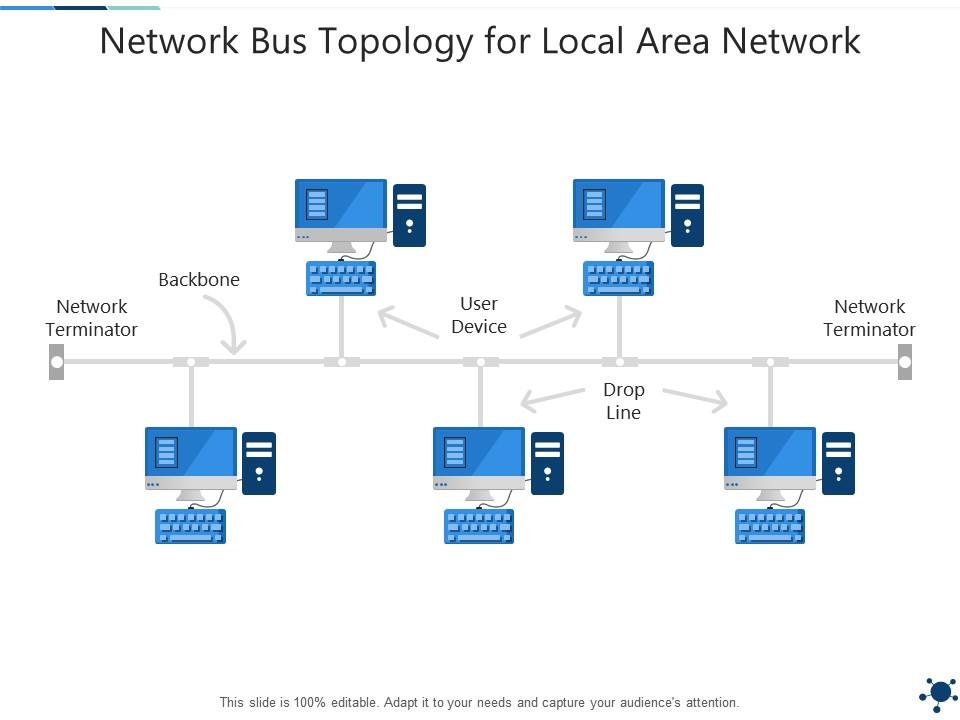
🔸 1. Bus Topology
- All devices connected to one main cable
- 📉 Cheap but if cable fails, network goes down
Example: Imagine one electricity wire shared by all bulbs—cut the wire,
everything goes off.
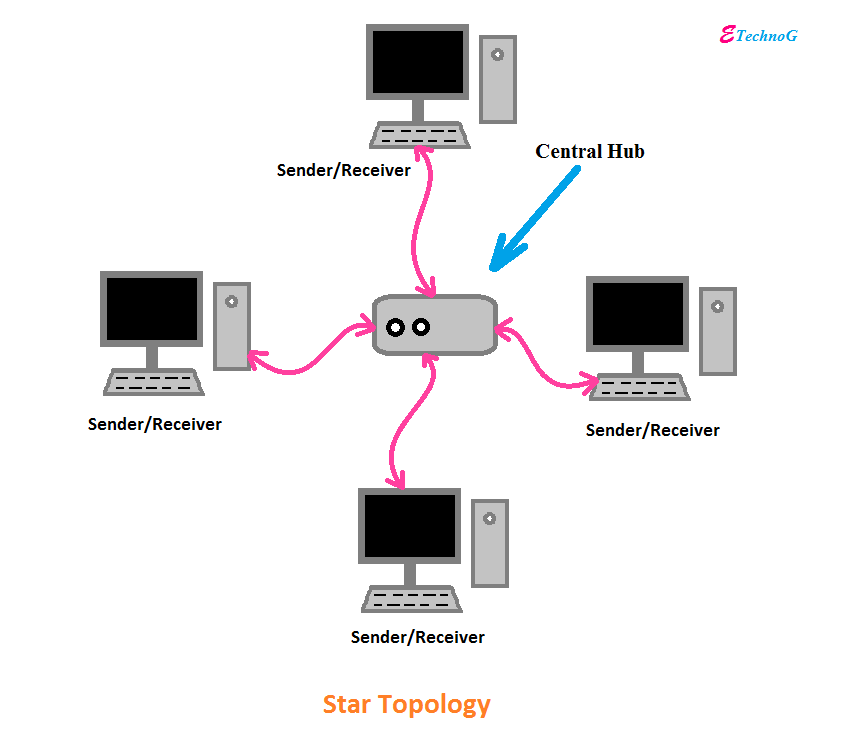
🔸 2. Star Topology
- All devices connected to a central device (hub/switch)
- 📈 Easy to manage; one failure doesn't crash the whole network
- 🔗 Central device is the hub
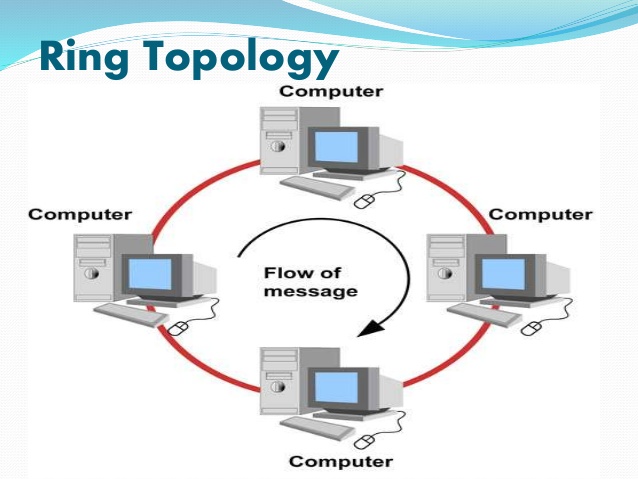
🔸 3. Ring Topology
- Each device connected to two others, forming a circle
- 🔁 Data moves in one direction (unidirectional) or both (bidirectional)
- 📉 If one device fails, it can disrupt the entire network
🔸 4. Mesh Topology
- Every device connected to every other device
- 💪 High redundancy; expensive and complex
Example: Everyone in a group chat directly messages everyone else.

🔸 5. Hybrid Topology
- Mix of two or more topologies (e.g., Star + Bus)
- Flexible and widely used in large networks

🔁
Transmission Modes
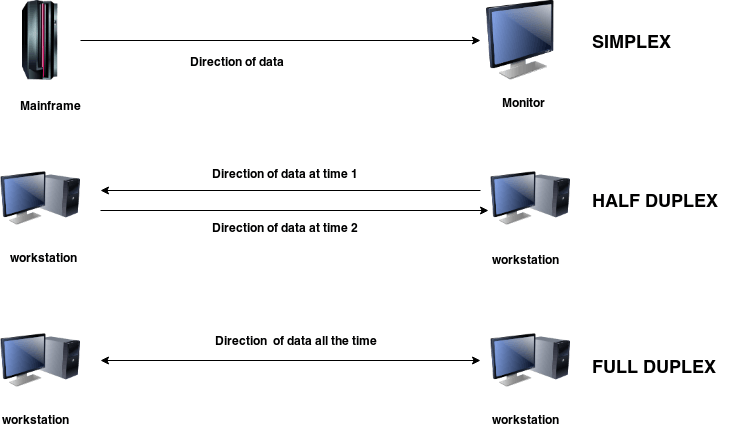
What is Transmission Mode?
Transmission Mode = Direction in which data flows.
| Mode | Direction | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Simplex | One-way | TV Broadcast |
| Half Duplex | Both ways, one at a time | Walkie-Talkie |
| Full Duplex | Both ways at the same time | Phone Call |
📶
Bandwidth vs Throughput vs Latency
| Term | Meaning (in computer network) | Real-World Example |
|---|---|---|
| Bandwidth | The maximum amount of data that can be transferred over a network in a given time. It defines the **capacity** of the network connection (measured in Mbps or Gbps). | You have a 100 Mbps internet plan — this is your bandwidth. |
| Throughput | The **actual** amount of data transferred successfully per second. Why it's less than bandwidth? – Because of congestion, errors, server speed, etc. | Though your plan is 100 Mbps, you are only getting 80 Mbps — that's the throughput. |
| Latency | The time it takes for a data packet to travel from source to destination and back (measured in milliseconds). | When you play an online game and experience lag — that's caused by high latency. |

📚
OSI Model vs TCP/IP Model
What are Reference Models?
Both are reference models used to understand how data travels over a network.


- OSI is a theoretical model
- TCP/IP is practical and used in real networks
- HTTP, FTP, DNS work on the Application layer
- IP (Internet Protocol) works on the Internet layer